Efficient Ways to Move Oil and Gas in 2025

The most efficient ways to move oil and gas in 2025 rely on advanced pipelines, marine vessels, railways, trucking fleets, and multi-modal solutions. Efficiency matters because speed, safety, cost, and environmental impact shape each decision. Recent studies show that pipelines handle large volumes quickly over long distances with low emissions. Marine transport reduces greenhouse gases when optimized, especially with wind-assisted propulsion. The table below compares speed, cost, fuel use, and emissions for different modes:
Transport Mode | Speed (Time) | Cost | Fuel Consumption (tonnes) | CO2 Emissions (tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Roadway | Fast | High | 658.47 | 1372.55 |
Railway | Moderate | Moderate | 568 | 365 |
Seaway | Slow | Low | Varies | Varies |
The oil and gas logistics guide highlights that the best method depends on distance, product type, and market conditions.
Key Takeaways
Pipelines are the most efficient way to transport oil and gas, offering high capacity and low emissions over long distances.
Marine transport is the most cost-effective option for international shipping, but it is slower than other methods.
Rail transport provides flexibility and can reach areas without pipeline access, making it a practical choice for medium distances.
Trucking is essential for last-mile delivery, allowing companies to quickly respond to market needs despite higher emissions.
Multi-modal logistics combines different transport methods to maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and improve safety in oil and gas supply chains.
Pipelines

Pipeline Efficiency
Pipelines move large volumes of oil and gas over long distances with unmatched efficiency. Companies in 2025 rely on advanced technologies to stay competitive. They use digital tools to improve operations and reduce delays. Many operators now integrate IoT, artificial intelligence, and data analytics. These tools help monitor flow rates, detect leaks, and optimize maintenance schedules. Real-time monitoring allows teams to respond quickly to any issues. As a result, pipelines deliver steady and reliable service.
Digital transformation drives efficiency.
IoT and AI improve safety and reduce downtime.
Real-time data supports better decision-making.
Safety and Risk
Pipeline safety remains a top priority. Operators face risks such as explosions, fires, and chemical exposure. Equipment failures and slips or falls also pose dangers. Companies address these risks by enforcing strict safety protocols and providing thorough training. Regular inspections and maintenance prevent equipment breakdowns. Emergency response plans ensure teams act fast during incidents. Workers use personal protective equipment and follow hazard identification procedures.
Explosions and fires: Prevented by safety protocols and trained teams.
Chemical exposure: Managed with proper gear and training.
Equipment failures: Reduced by regular checks.
Falls and trips: Minimized with safety equipment.
Emergency plans: Ready for quick action.
Cost and Investment
Building and maintaining pipelines requires significant investment. The average cost per mile for pipelines built before 2024 was $5.75 million. Since then, costs have risen by almost 90%. This increase leads to higher transportation expenses for oil and gas companies. Despite the cost, pipelines remain the most cost-effective option for moving large quantities over long distances.
Environmental Impact
Pipelines transport more oil than other methods, but they have a lower incident rate per million barrels than rail. From 2003 to 2013, pipelines had only 0.049 incidents per million barrels, while rail had 0.227. Experts note that rail transport causes double the environmental and health costs compared to pipelines. Pipelines also produce fewer emissions per unit moved.
Pipelines offer a safer and cleaner way to move oil and gas compared to rail.
Pipeline Innovations
Innovation Type | Key Benefits | Real-World Application |
|---|---|---|
Corrosion-free, lightweight, fatigue-resistant | Used in the Middle East and North Sea, reducing downtime | |
Nanotechnology-Enhanced Coatings | Improved durability, self-healing | Field trials show 30% better performance |
Smart Materials for Real-Time Monitoring | Detect stress and temperature changes | Fiber-optic liners tested in the Gulf region |
High-Performance Alloys | Superior corrosion resistance | Used in deepwater and high-sulfur fields |
Recyclable and Eco-Friendly Materials | Lower environmental footprint | Pilot project in North Africa cut lifecycle emissions by 40% |
Marine Transport

Cost-Effectiveness
Marine transport offers the lowest cost per tonne-kilometer for oil and gas in 2025. Tankers move large volumes across oceans at a fraction of the price compared to pipelines and railroads. The table below shows the cost comparison:
Transport Method | Cost (cents per tonne-km) |
|---|---|
Marine Tankers | 0.1 |
Pipelines | Higher due to fixed costs |
Railroads | In between |
Shipping by sea remains the most economical choice for international deliveries. Companies select marine transport when they need to balance cost and capacity.
International Shipping
Global oil and gas shipping faces several challenges. Geopolitical instability disrupts trade routes. Regulatory changes create uncertainty for operators. Labor shortages and volatile freight markets add complexity. Companies respond by adopting cloud technology and outsourcing non-core functions. AI-driven analytics help optimize routes and manage risks.
Geopolitical uncertainty affects trade routes.
Trade policies may increase tariffs and protectionist measures.
Regional conflicts can disrupt supply chains.
Shipping firms use technology to stay flexible and maintain reliable service.
Safety at Sea
Safety protocols for marine transport have advanced in recent years. Operators deploy containment booms that work in different water conditions. Oil-absorbing materials improve spill cleanup. Bioremediation techniques reduce environmental harm. Training programs focus on risk assessment and emergency response. Workers use virtual reality simulations to prepare for incidents. Regular safety audits and clear communication promote a strong safety culture.
Advanced containment booms
Oil-absorbing materials
Bioremediation techniques
Comprehensive training programs
Virtual reality and simulation-based training
Strong safety culture with audits
Environmental Regulations
International regulations require companies to monitor greenhouse gas emissions and fuel consumption for each ship. Ships must submit annual emissions reports verified by accredited MRV shipping verifiers. Vessels visiting European ports carry a document of compliance. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) sets strict rules under MARPOL Annex VI, aiming for net-zero emissions by 2050.
Regulation | Description |
|---|---|
MARPOL Annex VI | Sets targets for reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions |
MRV Requirements | Annual emissions reporting and verification for ships in the European area |
Marine Logistics Trends
Marine logistics in 2025 show rapid change. Companies adopt AI and automation to improve efficiency and reduce errors. Sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy and electric vehicles, help meet regulatory demands. Real-time visibility platforms connect warehouse management systems, giving operators instant updates and improving planning.
Trend | Description |
|---|---|
Enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and optimizes operations through predictive analysis and route planning | |
Sustainable Practices | Eco-friendly methods, renewable energy, and electric vehicles minimize environmental impact |
Visibility and Transparency | Real-time updates from integrated platforms improve customer trust and operational planning |
Marine transport continues to evolve, offering cost savings, safety improvements, and environmental benefits for oil and gas logistics.
Rail Transport
Flexibility and Reach
Rail transport offers strong flexibility for oil and gas logistics in 2025. Companies can quickly adapt to changing market demands and reach many destinations. Rail lines connect new production sites that lack pipeline infrastructure. Pipelines require major investment and follow fixed routes, limiting their ability to respond to market shifts. Rail provides a practical solution for moving oil from remote areas.
Rail adapts quickly to market changes.
Rail reaches locations without pipelines.
Pipelines have fixed routes and high expansion costs.
Safety Standards
Safety remains a top priority for rail operators. Recent data from the Federal Railroad Administration shows a 33% drop in train accident rates since 2005 and a 15% decrease in the last year. Class I railroads set record-low injury and fatality rates. New regulations require minimum crew sizes and certification for dispatchers and signal employees. Crews transporting hazardous materials must carry emergency escape breathing apparatus. The FRA also introduced tougher standards for new freight cars and fatigue risk management programs.
Accident rates continue to decline.
Crew certification and minimum sizes improve safety.
Emergency equipment protects workers.
Fatigue risk management reduces accidents.
Cost Structure
Rail transport can be more economical than pipelines for undiluted shipments. In 2025, moving bitumen or heavy oil by rail costs 12% to 31% less than committed pipelines. Rail does not need diluent for undiluted bitumen, which keeps costs low. Adding diluent increases rail costs and makes it less competitive. Key expenses include loading and unloading fees, terminal charges, and tank car leases.
Rail is cost-effective for undiluted shipments.
Diluent increases rail costs.
Main costs: loading, unloading, terminal fees, tank car leases.
Environmental Footprint
Rail transport moves one ton of goods about 470 miles on a single gallon of fuel. Trucks move the same load only 134 miles per gallon. Rail’s higher carrying capacity reduces traffic and eases strain on roads. However, spills and accidents remain a concern. In 2013, rail cars spilled 1.5 million gallons of crude oil, showing the risks involved.
Rail reduces emissions and traffic but requires strong safety measures to prevent spills.
Rail Innovations
Innovation Type | Description | Impact on Logistics |
|---|---|---|
Autonomous Trains | Driverless vehicles with sensors and AI for real-time monitoring | Improves throughput and reduces human error |
IoT-enabled Sensors | Smart sensors track load status, location, and environment | Enhances visibility and proactive response |
AI-driven Scheduling | Algorithms reschedule trains based on real-time demand | Increases efficiency and reduces delays |
Blockchain Integration | Secure digital ledger tracks materials from extraction to delivery | Ensures authenticity and compliance |
Green Locomotives | Electrification and sustainable practices | Reduces emissions and operational costs |
Digital Twins | Virtual models predict failures and optimize maintenance | Lowers outages and enhances safety |
Intermodal Terminals | Smart infrastructure for seamless transfer between transport modes | Enhances fluidity and reduces bottlenecks |
Trucking
Last-Mile Delivery
Trucking plays a vital role in oil and gas logistics by handling last-mile delivery. Companies depend on trucks to reach remote sites and final destinations where pipelines, rail, or ships cannot go. Drivers deliver products directly to refineries, storage facilities, and end users. This flexibility allows operators to respond quickly to changing market needs. Trucks provide reliable service for short distances and urgent shipments.
Safety Protocols
Safety remains a top concern in oil and gas trucking. Vehicle collisions cause four out of ten fatal injuries in the sector. Companies invest in comprehensive driver safety training and regular refreshers. They enforce strict rest breaks and monitor drivers for fatigue. Vehicles feature backup cameras and collision alarms to prevent accidents. Regular maintenance ensures trucks operate safely.
Driver safety training and refreshers
Enforcement of rest breaks and fatigue monitoring
Backup cameras and collision alarms
Routine vehicle maintenance
Cost Factors
Trucking costs depend on several key factors. Fuel prices remain a major expense, often affected by geopolitical events and supply chain disruptions. Unrest in oil-producing regions can lead to sudden price increases. Environmental policies may require investments in alternative fuel technologies or compliance measures.
Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Fuel Prices | Fuel remains a critical expense, with prices influenced by geopolitical events and supply chain disruptions. |
Geopolitical Tensions | Unrest in oil-producing regions can lead to fuel supply disruptions and sudden price increases. |
Environmental Policies | Stricter regulations may increase costs or necessitate investments in alternative fuel technologies. |
Emissions and Environment
Trucking emissions impact the environment more than other transport methods. Gasoline and diesel trucks produce higher emissions, but natural gas and electric trucks show lower numbers. Companies look for ways to reduce their carbon footprint by adopting cleaner technologies.
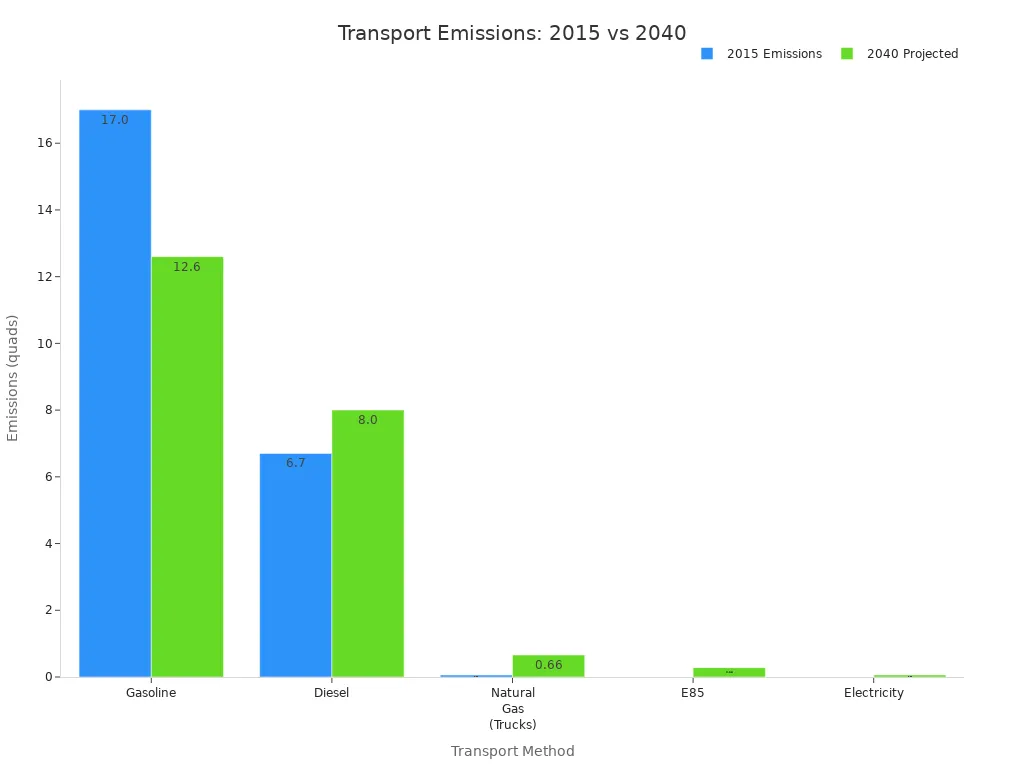
Transport Method | 2015 Emissions (quads) | 2040 Projected Emissions (quads) |
|---|---|---|
Gasoline | 17.0 | 12.6 |
Diesel | 6.7 | 8.0 |
Natural Gas (Trucks) | 0.06 | 0.66 |
E85 | N/A | 0.28 |
Electricity | N/A | 0.06 |
Companies invest in natural gas and electric trucks to lower emissions and meet environmental goals.
Trucking Trends
Oil and gas trucking in 2025 shows rapid change. Companies use AI for predictive maintenance, extending equipment life and reducing costs. IoT devices monitor vehicle performance and track shipments in real time. Advanced analytics help optimize production and logistics. Autonomous operations and sustainability practices continue to grow.
Trend | Description |
|---|---|
Predictive Maintenance | AI systems predict potential failures, extending equipment life and reducing replacement costs. |
Enhanced Safety and Security | IoT devices monitor vehicle performance and environmental conditions for safe deliveries. |
Streamlined Logistics | IoT analyzes data for optimized route planning and timely deliveries. |
Real-time Visibility | IoT enables real-time shipment tracking for proactive issue resolution. |
Cost Reduction | IoT optimizes logistics, leading to reduced costs through improved efficiency and minimized downtime. |
Trucking companies embrace technology to improve safety, reduce costs, and support sustainability.
Multi-Modal Logistics
Coordinating Transport Methods
Multi-modal logistics combines pipelines, marine, rail, and trucking to create a seamless oil and gas supply chain. Companies coordinate these transport methods to maximize efficiency and reduce costs. They use advanced technologies for real-time visibility and operational control. Logistics teams develop risk management strategies to handle disruptions and keep deliveries on schedule.
Multimodal transportation ensures efficient delivery across long distances.
Integration of digital tracking systems provides instant updates and helps manage disruptions.
Risk management strategies prepare teams for unexpected events.
Coordinating road, sea, rail, and air transport is essential for effective logistics. Real-time tracking systems enhance visibility and allow teams to respond quickly to changes.
Efficiency in Multi-Modal Solutions
Multi-modal solutions offer measurable efficiency gains for oil and gas logistics. Companies implement AI and machine learning to optimize supply chains and automate inventory management. These technologies can reduce operational costs by up to 20%. Logistics teams use predictive analytics to order replacement parts in advance, ensuring smooth operations. Digital transformation gives organizations real-time visibility into permits and automated alerts for conflicts, which reduces delays and improves safety oversight.
AI and machine learning optimize supply chains and automate inventory.
Predictive analytics help teams plan ahead and avoid disruptions.
Digital transformation improves safety and reduces permit-related delays.
Efficiency Factor | Impact on Logistics |
|---|---|
AI and Machine Learning | 20% reduction in operational costs |
Predictive Analytics | Smoother operations, fewer delays |
Real-Time Visibility | Improved safety and oversight |
Oil and Gas Logistics Guide: Choosing the Best Transport
The oil and gas logistics guide helps companies select the best transport method for each shipment. Decision factors include efficiency, cost, safety, and environmental impact. Pipelines offer high capacity and efficiency but require large investments. Trucks provide versatility but can be costly. Rail balances speed and cost, while each method has unique safety measures. Environmental risks also play a key role in the decision-making process.
Efficiency: Pipelines move large volumes quickly.
Cost: Rail and marine transport often reduce expenses for long distances.
Safety: Strict protocols protect workers and the environment.
Environmental Impact: Companies must consider emissions and spill risks.
The oil and gas logistics guide recommends evaluating distance, product type, and market conditions before choosing a transport method. Multi-modal logistics provides flexibility to adapt to supply chain changes and ensures customer satisfaction.
Comparing Methods
Speed vs. Cost
Transporting oil and gas in 2025 requires balancing speed and cost. Pipelines move products quickly over long distances, but they demand high upfront investment. Marine transport offers lower costs for large shipments, though ships travel slowly across oceans. Rail transport provides faster delivery than marine, with competitive costs for medium to long distances. Trucking delivers the fastest service for short hauls, but costs rise with fuel and maintenance.
Transport Method | Speed | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
Pipelines | Fast | High initial investment, cost-effective for large volumes |
Marine Transport | Slow | Most cost-effective for long-distance, high-volume shipments |
Rail Transport | Faster than marine | Competitive for medium to long distances, lower cost per ton-mile |
Trucking | Fast (short haul) | High cost for long distances, flexible for last-mile delivery |
Companies use the oil and gas logistics guide to match transport speed and cost with their business needs.
Safety Comparison
Safety records vary across transport methods. Pipelines show the lowest rates of spills and injuries. The Fraser Institute reports that pipelines experience fewer incidents than rail or truck. Pipelines average 0.6 spills per billion ton-miles, while rail averages 2 and trucking averages 20. Fatalities remain rare for pipeline workers, averaging 0.2 per year, compared to 81 per year in rail transport. Injuries requiring hospitalization occur 30 times more often in rail than in pipelines.
Pipelines: Lowest spill and injury rates
Rail: Higher injury and fatality rates
Trucking: Most frequent spills per ton-mile
Marine: Safety depends on weather and crew training
Environmental Impact
Each transport method affects the environment differently. Pipelines produce fewer emissions per unit moved and have a lower incident rate. Marine transport uses less fuel per ton-mile but faces risks from spills at sea. Rail reduces road congestion and emissions but can cause large spills in accidents. Trucking generates the highest emissions, especially with diesel engines. Companies invest in cleaner technologies to reduce their environmental footprint.
Choosing the right method helps companies meet sustainability goals and protect natural resources.
Practical Recommendations
Selecting the best transport method depends on shipment size, distance, and destination. Pipelines suit large, long-distance deliveries. Marine transport works best for international shipments. Rail offers flexibility for medium distances and remote locations. Trucking handles last-mile delivery and urgent shipments. Companies should review safety records, environmental impact, and cost before making decisions. The oil and gas logistics guide recommends combining methods for optimal efficiency and reliability.
Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|
Pipelines | Fast, safe, low emissions | High investment |
Marine | Cost-effective, global | Slow, spill risk |
Rail | Flexible, moderate cost | Accident risk |
Trucking | Last-mile, fast | High emissions |
Tip: Companies should match transport methods to shipment size, distance, and safety needs. They can combine options for better results.
Oil and gas logistics will keep improving with new technology and stronger safety standards.
FAQ
What is the safest way to transport oil and gas in 2025?
Pipelines show the lowest spill and injury rates. Companies use advanced monitoring systems and strict safety protocols. Workers receive regular training to prevent accidents.
How do companies reduce environmental impact during transport?
Operators invest in cleaner technologies, such as electric trucks and green locomotives. They follow strict regulations and use real-time monitoring to detect leaks quickly.
Which transport method costs the least for long distances?
Marine transport offers the lowest cost per tonne-kilometer for international shipments. Pipelines also provide cost savings for large volumes over land.
Why do companies use multi-modal logistics?
Multi-modal logistics combines pipelines, rail, marine, and trucking. This approach increases flexibility and efficiency. Teams use digital tracking to coordinate shipments and manage risks.
See Also
Enhancing Global Operations Through Innovative Logistics Strategies
PGL’s Knowledge Ensures Smooth Supply Chain Operations In America
Three Ways PGL Trucking Services Reduce Your Expenses
Streamlining USA Supply Chains With Global Logistics Solutions
Maximizing Global Efficiency With Point-to-Point Logistics Systems
