Understanding Common Logistics Challenges in the Energy Sector

You face many logistics challenges in energy sector operations. These include rising material costs, logistics complexities, supply chain disruptions, and emission reduction pressures. Supplier delays, inventory gaps, and poor warehouse practices can slow down projects. When logistics bottlenecks and labor shortages occur, operational costs rise and project schedules slip. Careful logistics planning boosts transportation efficiency and helps you meet sustainability goals. Smart choices in logistics support your success and keep energy projects on track.
Key Takeaways
Supply chain disruptions can delay energy projects and increase costs. Plan for risks to keep operations on track.
Transportation bottlenecks, often caused by infrastructure issues and labor shortages, can slow down projects. Address these challenges to avoid costly delays.
Labor shortages in the energy sector make it hard to find skilled workers. Invest in workforce development to build a strong team.
Cost pressures from rising material and transportation prices affect logistics. Manage these costs to maintain efficiency and competitiveness.
Sustainability demands require a shift to greener practices. Balance operational efficiency with environmental goals to succeed in the energy sector.
Logistics Challenges in Energy Sector

Supply Chain Disruptions
You often face supply chain disruptions in the energy sector. These disruptions can delay projects and increase costs. Many utility-scale solar projects planned for 2022 were postponed or cancelled because of these issues. In fact, 56% of such projects worldwide experienced delays. The main causes include production bottlenecks, mobility restrictions, factory closures, surging shipping costs, longer delivery times, and geopolitical conflicts like the Ukraine-Russia crisis. Energy uncertainty from climate disasters also adds to the problem.
Common causes of supply chain disruptions:
Production bottlenecks
Mobility restrictions
Factory closures
Surging shipping costs
Longer delivery times
Geopolitical conflicts
Energy uncertainty from climate disasters
You need to plan for these risks to keep your projects on track. Supply chain complexity makes logistics challenges in energy sector more difficult to manage.
Transportation Bottlenecks
Transportation bottlenecks slow down energy projects and raise costs. You see these bottlenecks most often at ports in developing economies, where facilities cannot meet growing demand. Operational bottlenecks happen when logistics providers cannot meet strict delivery schedules. Institutional bottlenecks result from weak national strategies that ignore freight logistics. Skills bottlenecks come from a lack of qualified workers in logistics roles.
Factors that contribute to transportation bottlenecks:
Unreliable suppliers and long lead times
Transportation delays and poor infrastructure
Sudden demand surges
Increased congestion
Labor shortages
Rising fuel costs
Higher customer expectations for fast delivery and tracking
You must address these logistics challenges in energy sector to avoid costly downtime and missed deadlines.
Infrastructure Limitations
Infrastructure limitations create major obstacles for energy logistics. Aging infrastructure struggles to meet rising demand. Capacity constraints in pipelines and transmission lines slow down growth. Regulatory challenges and public opposition make it hard to expand energy infrastructure.
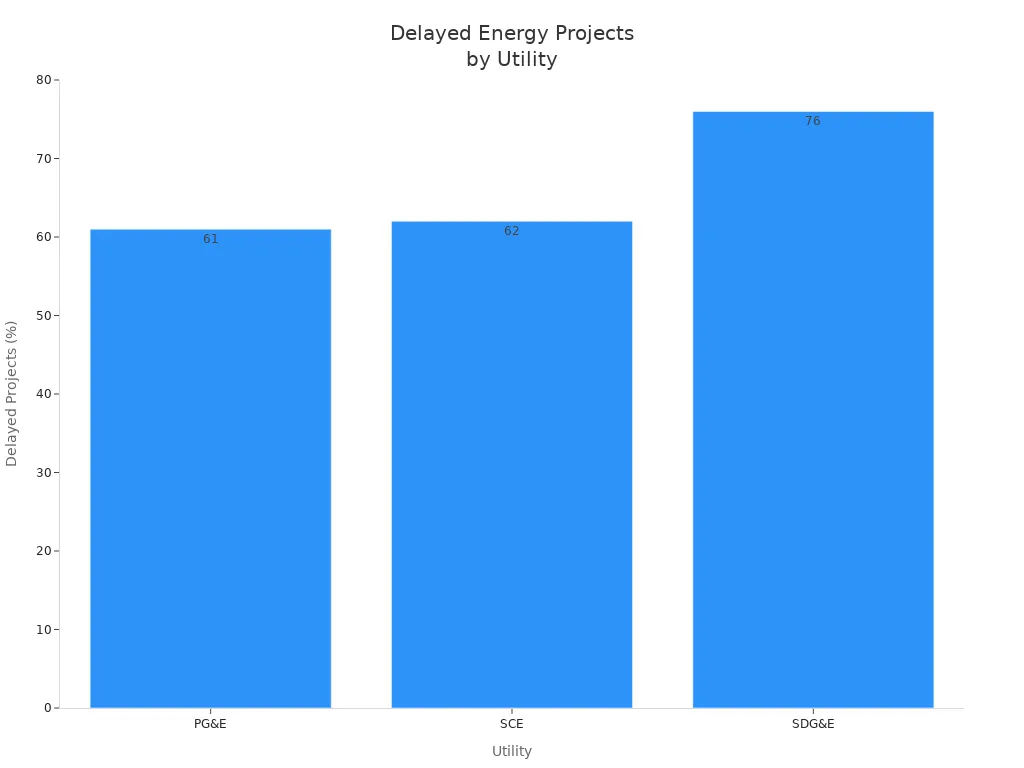
Utility | Main Reasons for Delay | |
|---|---|---|
PG&E | 61% | Prioritization (73%) |
SCE | 62% | Prioritization (24%), Permitting (21%) |
SDG&E | 76% | Permitting (63%), Construction Delays (26%) |
Type of Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
Aging Infrastructure | Energy infrastructure across North America is aging and struggling to meet growing demand. |
Capacity Constraints | Infrastructure bottlenecks, especially in natural gas pipelines and electric transmission lines, complicate growth. |
Regulatory Challenges | Public opposition and regulatory approvals are significant hurdles in expanding energy infrastructure. |
You need to overcome these infrastructure issues to reduce delays and improve logistics performance.
Regulatory Risks
Regulatory risks can disrupt logistics planning and execution. You face penalties and legal action if you do not comply with regulations. Vendor failures can interrupt operations and increase costs. Environmental compliance failures may result in loss of licenses.
Regulatory risks include:
Penalties and legal action for noncompliance
Operational interruptions from vendor failures
Supply chain disruptions due to vendor issues
Environmental compliance failures
Recent regulatory changes have affected logistics challenges in energy sector. The U.S. has imposed a 10% tariff on energy-related imports, including crude oil, natural gas, and electricity. These tariffs aim to address national security and economic imbalances.
Regulatory Change | Impact |
|---|---|
Reduction of regulatory burdens | Encourages investment in oil and natural gas by lowering costs and administrative hurdles. |
Implementation of tariffs on energy imports | Aims to reduce dependency on foreign energy and promote domestic production. |
Introduction of carbon pricing mechanisms | Encourages investment in renewable energy and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. |
Carbon pricing mechanisms, such as taxes or cap-and-trade systems, increase costs for greenhouse gas emissions. You must adapt your logistics strategies to meet these new requirements.
Labor Constraints
Labor shortages make logistics challenges in energy sector even harder. You may struggle to find skilled workers for renewable energy jobs. In Canada, over 13% of renewable energy jobs were unfilled in 2023, much higher than the 2% rate in other trades. Globally, 76% of employers in energy and utilities report difficulty finding skilled talent. In the electric vehicle and battery sector, 82% of professionals note a shortage of skilled local applicants, especially in upstream supply chain roles.
Labor shortage facts:
Over 13% of renewable energy jobs in Canada were unfilled in 2023
76% of global energy and utilities employers report talent shortages
82% of electric vehicle and battery professionals see a lack of skilled local applicants
You need to invest in workforce development to overcome these labor constraints.
Cost Pressures
Cost pressures affect every part of energy logistics. You pay more for raw materials, transportation, labor, and manufacturing. Rising energy prices and material shortages increase operational costs. Inflation pushes up the price of finished goods, making it harder for you to stay competitive.
Cost Pressure | Description |
|---|---|
Increased Procurement Costs | The cost of acquiring raw materials and goods has risen sharply, impacting procurement budgets. Companies are paying more for everything from raw materials to finished products. |
Higher Transportation and Shipping Costs | Transportation costs, especially for international shipments, have soared due to rising fuel prices, shipping delays, and labor shortages in the logistics sector. |
Rising Labor Costs | Labor costs have increased across industries, particularly for essential workers in warehouses, logistics, and manufacturing, necessitating higher wages to attract and retain skilled workers. |
Increased Manufacturing and Operational Costs | Rising energy prices and material shortages are raising manufacturing costs, particularly in sectors that rely on energy-intensive production processes. |
Rising Prices for Finished Goods | As inflation pushes up the costs of raw materials, labor, transportation, and energy, businesses are being forced to increase the prices of their products, impacting price-sensitive industries. |
You must manage these cost pressures to keep your logistics operations efficient.
Sustainability Demands
Sustainability demands are changing how you manage logistics challenges in energy sector. You need to transition to renewable energy and adopt greener practices. Stricter emissions standards and carbon taxes require you to comply with new regulations. Companies now electrify transport and use renewable energy in their facilities to reduce environmental impact.
Common sustainability demands:
Transition to renewable energy
Stricter emissions standards and carbon taxation
Electrification of transport
Use of renewable energy in facilities
You must balance sustainability goals with operational efficiency to succeed in today’s energy sector.
Case Studies and Examples

Oil & Gas Logistics
You see many logistics challenges in energy sector operations, especially in oil and gas. Companies have faced delays and higher costs when supply vessels cannot reach rigs on time. Sometimes, you must hire spot vessels at premium rates to deliver emergency materials. Fixed berthing slots and limited rig resources often cause supply vessel delays. The bullwhip effect can lead to idle time for vessels and wasted fuel.
Vessel speed optimization helps you save fuel and reduce emissions. Slow steaming and Just-in-Time arrival at rigs can cut fuel use by over 7%.
Remote monitoring with AR/VR, IIoT sensors, and drones lets you inspect equipment without sending workers, lowering aviation costs.
Cloud-enabled collaboration gives you real-time data access, improving coordination with suppliers.
Agentic AI predicts disruptions and helps you make better decisions.
Shell used AI and machine learning to monitor asset health. You can reduce unplanned downtime by 20% and maintenance costs by 15% with these tools.
Renewable Energy Projects
You face unique logistics challenges in energy sector projects like wind and solar farms. Oversized and fragile cargo needs special handling and equipment. You must coordinate with many suppliers and stakeholders. Regulatory compliance is important for customs, safety, and environmental rules. Tight deadlines require fast deliveries and smooth coordination. Companies now focus on carbon-neutral transportation and route optimization to meet sustainability goals.
Infrastructure bottlenecks, such as limited warehouse space and weak transport networks, can delay projects.
Labor shortages, especially for truck drivers and skilled workers, slow down deliveries.
Developers secure contracts at fixed prices to manage material shortages, but rising costs can affect project returns.
Strategic planning, workforce automation, and supply chain management help you anticipate and reduce supply risks.
Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
Strategic Planning | You plan ahead to avoid supply risks. |
Workforce Automation | Automation boosts efficiency and reduces reliance on scarce materials. |
Supply Chain Management | You adapt supply chains to handle vulnerabilities and global tensions. |
Global Supply Chain Issues
You have seen global supply chain issues affect energy projects in recent years. Volatility in raw material supply and prices, such as polysilicon, steel, copper, and aluminum, has caused problems. Polysilicon prices rose by 350% between 2020 and June 2022. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed weaknesses in supply chains, especially for materials from China. Geopolitical tensions, like the Ukraine crisis, increased costs for raw materials. Limited manufacturing and installation capacity, such as a shortage of vessels for offshore wind turbines, also creates delays. Strategic partnerships between developers and manufacturers help you build resilient supply chains.
Issue | Description |
|---|---|
Volatility in raw material supply and prices | Prices for key materials can change quickly, making planning hard. |
COVID-19 pandemic disruptions | Supply chains broke down, especially for materials from China. |
Geopolitical tensions | Conflicts like the Ukraine crisis raise costs and cause delays. |
Limited manufacturing and installation capacity | Not enough vessels for installing offshore wind turbines. |
Need for strategic partnerships | Partnerships help you strengthen supply chains and reduce risks. |
Solutions to Logistics Challenges
Technology Adoption
You can solve many logistics problems by using new technology. Electric vehicles and trucks help you deliver goods with less pollution. LNG-fueled ships also lower emissions. Digital tools let you track shipments and manage compliance. Sustainable packaging reduces waste. Energy-efficient warehouses save money and cut emissions. The table below shows how these technologies work in logistics:
Technology | Application in Logistics |
|---|---|
Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Used for last-mile delivery and long-haul transport |
Alternative Fuel Vehicles | Includes electric trucks and LNG-fueled ships |
Improve traceability and compliance management | |
Sustainable Packaging | Minimizes waste and enhances sustainability |
Energy Efficiency Enhancements | Applied in warehouses to reduce emissions and operating costs |
Digital solutions boost efficiency and help you lower greenhouse gas emissions. Companies see better energy use and more green innovation when they use these tools.
Collaboration Strategies
You improve supply chain resilience by working with other companies and logistics providers. Sharing resources helps you respond to disasters faster. Real-time communication lets you solve problems quickly. You can share warehouse space and truck capacity during disruptions. Pre-positioning supplies and using flexible transportation plans make your operations stronger. Partnerships with award-winning companies like Dimerco and Echo Global Logistics show how teamwork leads to greener and more reliable logistics.
Sustainable Practices
You can lower your carbon footprint by using clean energy and smart transportation systems. Electric trucks and vans, biodiesel, and hydrogen-powered vehicles help you move goods with less pollution. Advanced route planning and shipment consolidation reduce fuel use and emissions. AI and machine learning make your supply chain more efficient. Using renewable energy in warehouses also cuts your reliance on fossil fuels.
Tip: Route optimization and shipment consolidation help you save money and protect the environment.
Workforce Development
You need skilled workers to keep your logistics running smoothly. Programs like NIICA’s apprenticeships and the National Talent Hub connect you with training and job opportunities. Stakeholder-led initiatives fill gaps in workforce development. Training and upskilling help your team learn new skills and adapt to new technology. Over 64% of energy companies invest in workforce training to close skills gaps. When you support employee growth, you improve retention and build a stronger team.
You face many obstacles in energy logistics. Supply chain disruptions, transportation delays, and labor shortages can slow down your projects. Cost pressures and sustainability demands also shape your decisions. You need to use new technology and build strong partnerships. Stay flexible and keep learning about new solutions. Take action to improve your logistics and reach your goals.
Explore more resources to stay ahead.
Connect with experts for advice.
Start planning for future challenges.
Tip: Small changes in your logistics can lead to big results.
FAQ
What is the biggest logistics challenge in the energy sector?
You often face supply chain disruptions. These can delay projects and raise costs. Weather, global events, and material shortages make planning hard. You need to stay flexible and prepare for sudden changes.
How can you reduce transportation delays in energy projects?
You can use route optimization tools and real-time tracking. These help you avoid bottlenecks and keep deliveries on schedule. Working with reliable partners also improves your results.
Why is sustainability important in energy logistics?
Sustainability helps you meet new rules and protect the environment. Using clean energy and efficient transport lowers emissions. Many customers and investors now expect green practices.
What skills do workers need in energy logistics?
Workers need technical skills, problem-solving abilities, and safety training. Digital tools and automation are common, so you must learn new technology. Good teamwork and communication also help you succeed.
How does technology improve energy logistics?
Digital tools let you track shipments, manage inventory, and predict problems. Automation speeds up tasks and reduces errors. Technology helps you save time, cut costs, and meet your goals.
See Also
Key Strategies for Effective Global Logistics Operations
The Role of Direct Logistics in Enhancing Global Efficiency
Transforming International Operations Through Innovative Logistics Solutions
Streamlining Supply Chains in the USA with Global Logistics
PGL’s Knowledge Ensures Smooth Operations for American Supply Chains
