Oil and gas logistics operations explained simply

Oil and gas logistics operations help you get the fuel and energy you use every day. These operations move oil and gas from where they are found to where you need them. Imagine a relay race, where each runner passes the baton smoothly so the team wins. In your world, oil supplies 34% of all energy and natural gas meets 25% of global demand. Without smooth logistics, energy would not reach your home, car, or workplace.
Key Takeaways
Oil and gas logistics operations ensure energy reaches homes, cars, and workplaces efficiently.
Key activities include procurement, transportation, storage, and distribution of oil and gas.
Safety is crucial; companies follow strict regulations to protect workers and the environment.
Technology like AI and digitalization improves efficiency and reduces costs in logistics operations.
Effective supply chain management helps prevent delays and ensures a steady flow of energy.
What are oil and gas logistics operations?

Simple definition
You can think of oil and gas logistics operations as the system that moves oil and gas from where they are found to where you use them. This system manages the transportation, storage, and handling of materials, equipment, and products in the oil and gas industry. You see the results every time you fill your car with gas or turn on the heat at home.
Oil and gas logistics operations keep the supply chain running smoothly. They help companies meet deadlines and follow strict safety and environmental rules.
Here is a simple table that shows how leading organizations define these operations:
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Definition | Oil and gas logistics refers to the specialized management and transportation of goods, equipment, and materials used in the extraction, production, and distribution of oil and gas. |
Importance | Efficient logistics is crucial for maintaining supply chain continuity and meeting production deadlines in a highly regulated industry. |
Operations Involved | Involves coordinating storage, inventory management, and compliance with environmental regulations, ensuring safe and timely transportation. |
Main activities
Oil and gas logistics operations include several main activities. Each activity plays a key role in making sure oil and gas reach you safely and on time.
Procurement: You need to get the right equipment, tools, and materials for drilling and production. This step makes sure everything is ready before work begins.
Transportation: You move oil, gas, and equipment from one place to another. Trucks, ships, pipelines, and trains help carry these materials across long distances.
Storage: You keep oil and gas in tanks or warehouses until they are needed. Safe storage prevents leaks and keeps products ready for delivery.
Distribution: You deliver refined products like gasoline and diesel to gas stations, factories, and homes. This step connects the supply chain to everyday life.
Industry experts divide these activities into three main sectors. Each sector has its own challenges and tasks:
Category | Main Activities |
|---|---|
Upstream | Move equipment, materials, and personnel to remote or offshore exploration and drilling sites. Manage rig moves, expedite shipments, and reach consolidation points for maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) materials. |
Midstream | Safely and efficiently transport and store crude oil and natural gas between extraction and refining. Manage oil country tubular goods (OCTG), coordinate with engineering and construction firms, execute multimodal transport strategies. |
Downstream | Ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards while managing turnarounds, capital project logistics, warehousing, and distribution of refined products like gasoline, diesel, and lubricants. |
You see differences in each sector. Upstream focuses on finding and producing oil and gas. Midstream handles moving and storing these resources. Downstream refines oil and gas and delivers products to you.
Recent technology has changed how you experience oil and gas logistics operations. Here are some important advancements:
Digitalization and automation help you track shipments and manage inventory in real time.
Artificial intelligence solves complex problems and improves efficiency.
Hydraulic fracturing lets you access new oil and gas sources.
Robotics and drones inspect equipment and keep workers safe.
Renewable energy integration reduces emissions and lowers costs.
Oil and gas logistics operations also affect the environment. Companies must protect habitats, prevent air and water pollution, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. You benefit when companies use safer and cleaner methods.
Key components of logistics

Transportation
You see transportation as the backbone of oil and gas logistics operations. Pipelines move most oil and gas across continents, with over a million miles in use worldwide. Ships and barges carry oil between countries, especially when you need to import energy from overseas. Railways offer a cost-effective way to move oil when building new pipelines is not possible. Trucks deliver oil and gas over short distances, often from remote sites to local markets. Each method helps you get energy where you need it, whether at home or at work.
Pipelines handle the largest share of global oil and gas movement. Ships and barges are vital for international trade. Railways and trucks fill in the gaps, making sure no location is left out.
Storage
You rely on storage to keep oil and gas safe until you need them. Storage facilities act as a buffer, protecting you from supply disruptions and helping companies manage inventory. Underground storage sites in the U.S. hold up to 3.5 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, while Canada’s facilities store 440 billion cubic feet. Crude oil sits in tanks that range from a few hundred to several thousand barrels. Supertankers can store more than 2 million barrels. Common types of tanks include fixed roof, floating roof, spherical, and horizontal tanks. Each type offers advantages like cost-effectiveness, quick installation, and environmental sustainability.
Fixed roof tanks work well for regular petroleum products.
Floating roof tanks help prevent vapor loss and fire hazards.
Spherical tanks store liquefied gases under high pressure.
Horizontal tanks suit smaller storage needs and can be moved easily.
Handling and distribution
You face several challenges when handling and distributing oil and gas. Many production sites sit in remote areas, so companies must invest in roads and infrastructure. Environmental risks, such as spills and leaks, require strict safety rules. Different regions have their own regulations, making compliance a constant task. High operational costs and changing oil prices also affect budgets.
Description | |
|---|---|
Local Distribution Companies | Utilities owned by investors or local governments. |
Regulation Authority | States and localities set rules for retail sales and distribution. |
Operational Issues | Includes customer rates, curtailment, balancing, and service terms. |
Safety Regulations | Compliance with PHMSA safety and security rules for natural gas lines. |
Supply chain management
You see supply chain management as the glue that holds oil and gas logistics operations together. The industry is complex and unpredictable, so companies must coordinate procurement, transportation, storage, and distribution. Strong supplier relationships help ensure a steady flow of raw materials. Effective procurement strategies reduce costs and speed up delivery. The global nature of oil and gas means companies must deal with risks like geopolitical instability and natural disasters. Digital technology, such as artificial intelligence and IoT, helps companies monitor operations in real time, avoid costly disruptions, and improve efficiency.
Digitalization can save upstream companies billions each year.
Advanced analytics help prevent supply chain problems.
Machine learning and IoT lower production costs and improve safety.
Importance of oil and gas logistics operations
Safety
You depend on safe oil and gas logistics operations to protect workers, communities, and the environment. Many risks exist, such as explosions, fires, equipment failure, and chemical spills. Companies use strict safety rules, regular training, and advanced technology to lower these risks. You can see the most common safety incidents in the table below:
Incident Type | Frequency | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
Pressure pumping | 9 | 1.9% |
Wellsite construction or upkeep | 8 | 1.7% |
Chemical handling | 7 | 1.5% |
Lease operation | 7 | 1.5% |
Spotting | 6 | 1.3% |
Office and administrative activities | 5 | 1.1% |
Training | 5 | 1.1% |
Well cleanout | 5 | 1.1% |
Wireline and slickline activities | 4 | 0.9% |
Vehicle incidents | 41 | N/A |
Explosions | 29 | N/A |
Other incidents (electrocution, etc.) | 2 each | N/A |
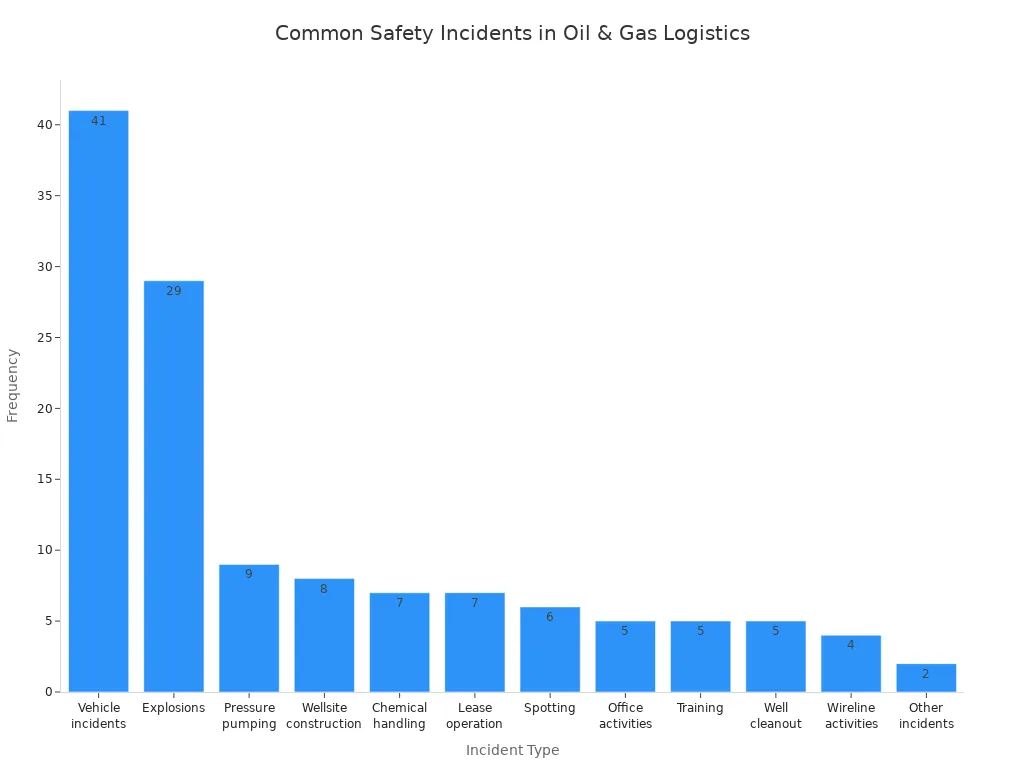
You see companies follow safety regulations, such as the Directive on Safety of Offshore Oil and Gas Operations, to prevent accidents and protect nature. Regular inspections, emergency plans, and strong safety equipment help keep everyone safe.
Efficiency and reliability
You rely on efficient and reliable oil and gas logistics operations to keep energy flowing without delays. Companies use smart strategies like route optimization and control towers to track shipments and avoid problems. You benefit from steady supplies and fewer disruptions. Here are some ways companies improve reliability:
Diversify suppliers and transport routes.
Use risk management to prepare for surprises.
Build resilience to handle market changes.
Logistics Strategy | Impact on Reliability |
|---|---|
Route Optimization | Enhances timely delivery and reduces costs |
Transportation Modalities | Balances speed, cost, and environment |
Control Towers | Improves visibility and reduces disruptions |
Key performance indicators help companies measure efficiency. You see better asset use, higher workforce productivity, and lower energy consumption. These improvements mean you get energy when you need it, and companies avoid costly delays.
Cost-effectiveness
You benefit when companies keep logistics costs low. Oil and gas logistics operations make up 5 to 15 percent of total production costs. Companies use new technology, such as sensors, cloud data, and artificial intelligence, to save money. For example, Shell uses AI to monitor equipment health, which has cut unplanned downtime by 20 percent and reduced maintenance costs by 15 percent.
Here are some top strategies for lowering logistics costs:
Use sensors and drones for real-time data.
Move data to the cloud for easy access.
Analyze big data to predict demand.
Automate tasks with robotics and digital twins.
Apply AI and machine learning for better planning.
Efficient logistics support millions of jobs and help keep prices stable. You see the impact in your daily life, from steady fuel prices to reliable public services.
Real-world examples
Crude oil transport
You see crude oil travel long distances before it reaches a refinery. Imagine oil pumped from a field in Texas. Trucks carry it to a rail terminal. Trains move it across states. Barges float it down rivers. Each step faces challenges. You notice that managing many carriers can cause confusion. Companies solve this by working with third-party logistics providers. These experts centralize transportation and make sure every shipment stays on track. You also see companies use transportation management systems. These systems give real-time updates and help avoid delays. Sometimes, moving oil by truck costs more. Companies switch to rail or barge to save money. Freight management becomes easier when experts handle the details.
Logistical Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
Decentralized transportation management | Partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) to centralize management. |
Lack of visibility | Implementing centralized transportation management systems (TMS) for better oversight. |
Reliance on over-the-road carriers | Exploring alternative transportation modes like rail and barge for cost-effectiveness. |
Need for optimized freight management | Utilizing 3PLs to manage and optimize freight moves effectively. |
You benefit from these solutions because they help companies deliver oil safely and on time.
Natural gas delivery
You rely on natural gas for heating and cooking. In some places, pipelines do not reach every home or business. Companies use a "virtual pipeline" to solve this problem. Trucks, trains, or ships carry compressed natural gas to areas without pipeline access. This flexible method adapts to your local needs. You see compressed natural gas used for road and rail transport. It helps deliver energy to remote towns and factories.
Logistics operations make sure gas moves safely and efficiently.
Real-time tracking and automated inventory systems keep deliveries on schedule.
Transportation, storage, and processing follow strict safety rules.
The natural gas supply chain includes processing, transportation, and storage.
You get reliable energy because companies use advanced technology and follow safety guidelines.
You see how logistics help move energy from remote sites to your home. Efficient delivery of equipment and water management support drilling and fracking. Outsourcing tasks like water hauling saves money and keeps companies focused.
Remote locations and regulations challenge logistics teams
Third-party experts improve compliance and reduce costs
How Logistics Support the Economy | Impact |
|---|---|
Reliable energy transportation | Keeps factories and transport running |
Supports families worldwide | |
Revenue for nations | Funds schools and hospitals |
Smooth supply management | Prevents energy shortages |
You notice new trends like digital technology and intermodal transport making logistics faster and greener. Real-time monitoring boosts efficiency, and natural gas systems replace older power plants. Logistics keep your world moving, powering daily life and the global economy.
FAQ
What does oil and gas logistics mean for you?
Oil and gas logistics means you get fuel and energy when you need them. These operations move oil and gas from where companies find them to your home, school, or workplace.
How do companies keep oil and gas safe during transport?
Companies use strong tanks, pipelines, and safety checks. You see workers follow rules to prevent leaks and accidents. Regular inspections help protect people and nature.
Why do oil and gas prices change?
Prices change because of supply, demand, and transport costs. If a storm blocks a pipeline, you might pay more. When companies find new sources, prices can drop.
What jobs can you find in oil and gas logistics?
You can work as a truck driver, warehouse manager, safety inspector, or logistics planner. Many jobs help move, store, and deliver oil and gas safely.
How does technology help oil and gas logistics?
Technology lets you track shipments, predict problems, and improve safety. Companies use sensors, drones, and computers to make sure oil and gas reach you quickly and safely.
See Also
Enhancing Global Operations With Innovative Logistics Strategies
Key Strategies For Effective Global Logistics Administration
Boosting Global Efficiency Through Point-to-Point Logistics
