What Are Domestic Freight Operations and How Do They Work

Domestic freight operations mean moving goods inside a country’s borders. In the United States, you see shipments travel from one state to another or within a state using trucks, trains, or combined methods. You play a vital role in supply chains when you understand how these shipments work. Most freight in the U.S. stays domestic, as shown below:
Year | Domestic Freight Percentage |
|---|---|
2035 | |
2002 | 91.4% |
Key Takeaways
Domestic freight operations move goods within a country, playing a crucial role in supply chains.
Understanding the different shipping methods, like Full Truckload (FTL) and Less Than Truckload (LTL), helps you choose the best option for your needs.
Technology, such as route planning software and real-time tracking, enhances efficiency and reliability in freight operations.
Selecting a freight provider with strong coverage and good customer service ensures timely deliveries and satisfied customers.
Analyzing costs based on distance, shipment size, and transportation mode helps you make informed decisions and save money.
Understanding Domestic Freight Operations

What Is Domestic Freight
You use domestic freight operations to move goods from one place to another within your country. These operations help you get products to stores, factories, and homes. You see many types of goods shipped, such as electronics, furniture, food, and even heavy machinery. Different types of trucks and trailers carry these items. For example:
Dry vans move consumer goods, electronics, and non-perishable foods.
Tankers transport liquids like corn syrup or petroleum.
Flatbeds carry lumber, construction materials, and equipment.
Special trailers, like drop decks or removable goosenecks, handle oversized or heavy cargo.
Domestic freight operations play several important roles in your national logistics network. Here is a table that shows the main functions:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
Transportation | Management of different transportation methods (road, rail, air) for efficient goods movement. |
Warehousing | Storage of goods to ensure availability for distribution. |
Distribution | Transfer of goods from warehouses to final destinations. |
Supply Chain Management | Coordination of all logistics processes to optimize the flow of goods. |
Management Roles | Involvement of operations, distribution, and inventory managers to oversee logistics activities. |
You also benefit from technology in these operations. Route planning software and GPS tracking help you move goods faster and more efficiently.
Domestic vs. International Shipping
You might wonder how domestic freight operations differ from international shipping. Domestic shipping keeps your goods inside your country’s borders. International shipping sends goods across borders to other countries.
You face fewer rules and less paperwork with domestic freight. You usually need a commercial invoice or packing list. International shipping requires more documents, such as Schedule B or Harmonized System (HS) codes. You must also follow the import laws of the destination country and fill out customs declaration forms. Domestic shipments move faster and do not need customs checks.
Transit times also differ. Here is a table that compares shipping methods and how long they take:
Shipping Method | |
|---|---|
Road Freight | 1-7 |
Air Freight | 1-5 |
Express | 2-5 |
Rail Freight | 10-30 |
Sea Freight (FCL/LCL) | 14-42 |
Sea Freight (International) | 20-60 |
Air Freight (International) | 1-10 |
You see that domestic freight operations usually deliver goods faster than international shipping.
Key Players and Roles
You interact with many key players in domestic freight operations. Each one has a special job to help your goods reach their destination. Here are some of the main companies and their roles:
Key Player | Role Description | Revenue (2023) |
|---|---|---|
FedEx Freight | Major carrier specializing in less-than-truckload (LTL) services, consolidating smaller shipments. | $9.2 billion |
XPO Logistics | Focuses on both LTL and full truckload services, using data analytics for route optimization. | $7 billion |
Knight-Swift Transportation | Leads in full truckload segment, leveraging economies of scale with a large fleet. | $6.9 billion |
Schneider National | Expertise in intermodal transportation, integrating trucking with rail services. | >$5 billion |
C.H. Robinson Worldwide | Largest freight broker, connecting shippers and carriers with a tech-driven approach. | $26 billion |
Echo Global Logistics | Provides managed transportation services, helping SMEs compete in logistics. | $3 billion |
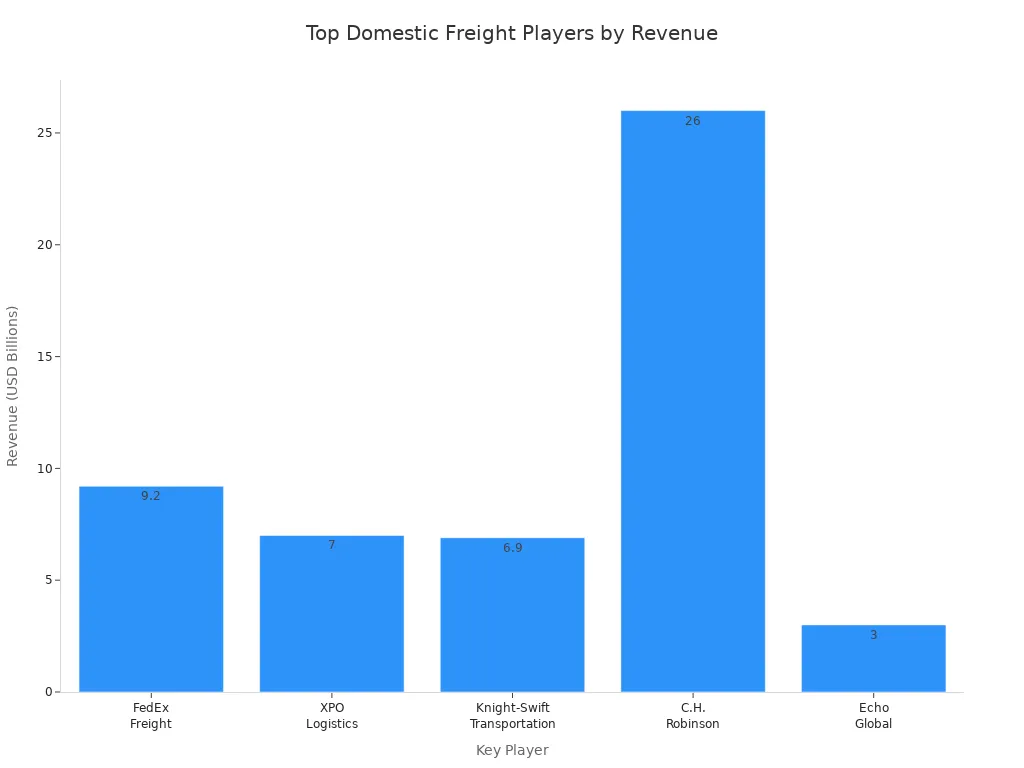
You also find other important roles in the process:
Shippers: You or your business send goods to customers or stores.
Carriers: Trucking, rail, or air companies move your goods.
Freight brokers: These experts connect you with the right carrier for your shipment.
Warehouse managers: They store and organize your goods before delivery.
Operations managers: They plan and oversee the entire shipping process.
Most of the U.S. market belongs to the top 25 carriers, who control about 91% of the less-than-truckload (LTL) market. This strong presence allows them to invest in better technology and larger networks, making your shipments more reliable.
Tip: When you understand the roles of each player, you can choose the best partners for your shipping needs and improve your supply chain.
Domestic Freight Operations Process

Domestic freight operations follow a clear process to move your goods from the starting point to the final destination. You can better manage your shipments when you understand each step.
Pickup and Origin Handling
The journey begins with the pickup of your goods. A carrier collects your shipment from your business, warehouse, or manufacturing site. This stage often faces a few challenges that can affect timing and cost.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Shipping Cost | Shipping companies may add fuel surcharges and other fees, making it hard to find competitive rates. |
Trailer Availability | Finding an available trailer can be tough, especially when demand is high. |
Seasonal Demand | Busy seasons can strain capacity and raise prices. |
You might notice that shipping costs change with fuel prices. During peak seasons, like holidays, you may struggle to find trailers. Planning ahead helps you avoid delays and extra charges.
Sorting and Consolidation
After pickup, your shipment travels to a freight terminal or warehouse. Here, workers sort and consolidate goods. If you ship less than a full truckload, your items get grouped with others heading in the same direction. This step improves efficiency and lowers costs.
Modern technology makes sorting and consolidation faster and more accurate. You benefit from systems like these:
Technology | Function |
|---|---|
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) | Gives you real-time updates, optimizes routes, and automates paperwork. |
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) | Tracks inventory, manages shipments, and streamlines the grouping of goods. |
These tools help you track your shipment and reduce errors during handling.
Main Transportation Modes
Once sorted, your goods move toward their destination using different transportation modes. You choose the best mode based on speed, cost, and the type of goods.
Transportation Mode | Delivery Time Characteristics |
|---|---|
Full Truckload (TL or FTL) | Fastest ground option, goes straight to the destination without extra stops. |
Less-than-truckload (LTL) | Slower, with more stops for loading and unloading. |
Intermodal Shipping | Combines road and rail, offers reliable delivery with strong rail networks. |
Expedited Ground | Moves freight quickly by minimizing stops and delays. |
Domestic Air | Fastest overall, best for urgent or high-value shipments. |
You can select a mode that matches your delivery needs. For example, air freight works well for urgent deliveries, while intermodal shipping balances speed and cost for larger shipments.
Final Delivery
The last step is final delivery, also called last-mile delivery. Your shipment leaves the regional terminal and heads to the customer’s door. This stage brings its own set of challenges:
Rising last mile delivery costs from fuel, overtime, and tolls.
Address mistakes can cause delays.
Route changes and unexpected orders disrupt schedules.
High delivery volumes during events or holidays make planning harder.
Weather and road conditions create unpredictability.
Missed deliveries mean extra trips and higher costs.
Tight deadlines leave little room for mistakes.
You can improve last-mile delivery by double-checking addresses, using route planning tools, and staying flexible with delivery times.
Tip: When you understand each step in domestic freight operations, you can spot problems early and make better choices for your business.
Service Types in Domestic Freight
Full Truckload (FTL)
You choose Full Truckload (FTL) when your shipment fills an entire truck. FTL works best for large shipments that need direct delivery. You avoid extra stops, so your goods arrive faster. Most FTL shipments carry between 24 and 34 standard pallets. Many trucks hold about 26 skids, and the total weight often reaches 42,000 to 45,000 pounds.
FTL shipment size ranges:
24 to 34 standard pallets
24 to 30 pallets for most shipments
About 26 skids per truck
FTL gives you control over timing and reduces the risk of damage. You pay for the whole truck, so this option suits businesses with high-volume needs.
Less Than Truckload (LTL)
You use Less Than Truckload (LTL) when your shipment does not fill a truck. LTL combines your goods with shipments from other businesses. This method saves you money if you ship less than 4,000 pounds. LTL works well for small businesses and lets you send smaller loads without paying for unused space.
Aspect | FTL Pricing | |
|---|---|---|
Cost Efficiency | More cost-efficient for smaller shipments (less than 4,000 pounds) | More economical for larger shipments (over 15,000 pounds) |
Shipment Size | Ideal for small businesses with less than truckload needs | Suitable for businesses needing to ship full truckloads |
Delivery Speed | May take longer due to multiple drop-offs | Generally faster as it goes directly to one destination |
Pricing Factors | Based on weight, freight class, density, stowability, handling characteristics, and liability | Based on distance, truckload capacity, weight, and additional services |
LTL may take longer because your goods stop at several locations. You benefit from lower costs and flexible shipping options.
Intermodal and Multimodal
You pick intermodal and multimodal services when you want to use more than one transportation mode. Intermodal shipping uses sealed containers that move between trucks, trains, or ships. Multimodal shipping lets you use different carriers for each leg of the journey. These services help you save money and protect your goods.
Flexibility for different shipping volumes
Improved security with sealed containers
Environmental sustainability by using efficient transport modes
Faster delivery times by combining transport options
Centralized responsibility for the whole shipping process
You gain more control and can adapt your shipping plans to fit your needs.
Expedited and Specialized Services
You need expedited or specialized services when your shipment is urgent or requires special handling. Expedited shipping moves your goods quickly, often for emergencies or last-minute orders. Specialized services protect fragile, high-value, or oversized items.
Description | |
|---|---|
Delicate electronics and devices | Items sensitive to bumps, such as medical devices and musical instruments. |
Fragile robotics and industrial equipment | Complex machinery needing extra protection from damage. |
Commercial refrigeration and restaurant equipment | Large, heavy items requiring padding to prevent damage. |
Fixtures, furniture, and miscellaneous fragile goods | Includes retail fixtures, antiques, and household items like mirrors and glass. |
Military freight | Requires specific paperwork and processes for transport. |
Motorcycles | Need enclosed transport and special handling to prevent damage. |
Tip: You use expedited shipping for supply chain challenges, emergencies, perishable goods, tight delivery timelines, and high-value freight.
You improve customer satisfaction and reduce risks when you choose the right service type for your shipment. Domestic freight operations offer many options to match your business needs.
Choosing a Freight Provider
Coverage and Network
You need a freight provider with strong coverage and a reliable network. A provider with nationwide reach saves you time and resources. You do not have to manage several carriers for different regions. Fast delivery options help you meet customer expectations, especially when people want same-day or next-day shipping. If your provider cannot deliver quickly, your customers may switch to competitors.
A reliable network also means fewer delays and better service. Look for these key metrics:
Metric | Importance |
|---|---|
On-time delivery | Over 90% on-time rate keeps your customers happy and loyal. |
Claims rate | Less than 1% shows your goods arrive safely and in good condition. |
Reschedule rate | Below 5% helps you avoid missed deliveries and extra costs. |
A strong delivery network is essential for both local and national businesses.
Choosing a carrier with broad coverage helps you grow your business.
Reliability and Technology
You want a provider that delivers on time and keeps you informed. Real-time tracking lets you see where your shipment is at any moment. This builds trust and helps you plan better. Providers that use predictive analytics can spot problems before they happen. They take action early to avoid delays.
Automation and AI in freight management make decisions faster and more accurate. These tools help your provider handle shipments smoothly and keep your business running without surprises.
Tip: Ask your provider about their tracking systems and how they use technology to prevent delays.
Pricing and Customer Service
You should understand how your provider sets prices. Most use a mix of base rates, extra fees, discounts, and surcharges. Here are some common pricing models:
Pricing Model | Description |
|---|---|
All or Nothing | You get low rates if you use the provider for all your shipments. |
Lowest Pricing | You pay the lowest price when there is plenty of space available. |
Value Pricing | You get good service at a fair price, not the cheapest but reliable. |
Three Party Pricing | An outside company negotiates rates for you and charges a fee. |
Cost Plus Pricing | You pay the provider’s cost plus a set fee, so you see exactly what you are paying for. |
Contracted prices give you stable rates for regular shipments.
Tariffs set a base price, but you may get discounts.
Dynamic rates change with the market.
Customer service ratings help you choose the right provider. High ratings show the provider is transparent and reliable. You can avoid delays and protect your reputation by picking a carrier with strong reviews.
Cost and Efficiency Factors
Distance and Shipment Size
You see freight costs change based on how far your shipment travels. Longer routes or remote destinations raise expenses because carriers need more fuel, time, and planning. The table below shows how distance affects cost:
Source | Insight |
|---|---|
uShip | Longer routes or less accessible destinations increase freight costs. |
TEU Inc. | Longer ship routes cost more. |
FreightPlus | The distance a shipment travels significantly influences costs. |
Maersk | Longer and/or more complex shipping routes increase costs. |
Shipment size also matters. You can save money and boost efficiency by choosing the right load type and packing your goods well. Here are some ways shipment size impacts efficiency:
Volume LTL gives you a middle ground between standard LTL and full truckload shipping.
You meet diverse customer needs while saving money and delivering on time.
Higher density shipments lower your freight charges.
Lower density shipments cost more.
Optimizing packaging and palletization increases freight density and efficiency.
Volume LTL helps you optimize space and reduce costs for larger shipments that do not fill a truck.
Mode and Timing
You pick a transportation mode based on cost, speed, and the type of goods. Each mode offers different benefits. The table below compares common options:
Metric | Truck Freight | Rail Freight | Ocean Freight | Air Freight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Average Cost | Moderate | Low | Very Low | Very High |
Typical Speed | Fast | Moderate | Very Slow | Very Fast |
Best For | Local, urgent | Long-haul, bulk | Bulk, low urgency | Urgent, high-value |
You match the mode to your needs. Fragile items may need air freight for security. Smaller shipments use LTL services. Larger loads often go by rail or ocean. If you need speed, air freight works best. If time is not critical, rail or ocean saves money.
Technology and Best Practices
You improve efficiency by using smart technology and automation. These tools help you move goods faster and with fewer mistakes:
Smart systems like WMS, TMS, RFID, AI, and robotics boost speed and accuracy.
Real-time analytics and predictive insights help you make better decisions and fill orders quickly.
Optimizing warehouse layouts and transportation design cuts costs and reduces waste.
High-tech solutions, such as micro-fulfillment centers and AI-driven routing, make last-mile delivery faster and improve customer experience.
Sustainable practices, including route optimization and electric vehicles, lower costs and support eco-friendly logistics.
Tip: You can increase efficiency and save money by adopting new technology and following best practices in your freight operations.
You now understand domestic freight operations, from how goods move to choosing the right provider. You can boost efficiency by streamlining management and using technology like TMS. You improve results when you collaborate with partners and monitor industry trends. Try these steps:
Focus on customer value and reliable deliveries.
Invest in sustainable growth and smart systems.
Diversify your freight options for resilience.
Analyze data to spot and fix inefficiencies.
You make better logistics decisions when you apply these strategies.
FAQ
What is the difference between FTL and LTL shipping?
You choose Full Truckload (FTL) when your shipment fills an entire truck. Less Than Truckload (LTL) combines your goods with others. FTL works best for large loads. LTL saves money for smaller shipments.
How do you track your domestic freight shipment?
You use tracking numbers or online portals from your carrier. Many providers offer real-time updates. You see your shipment’s location and estimated delivery time. Tracking helps you plan and avoid surprises.
Which transportation mode is fastest for domestic freight?
You pick air freight for the fastest delivery. Trucks move goods quickly for short distances. Rail works well for heavy loads but takes longer. Air freight suits urgent shipments and high-value items.
What factors affect the cost of domestic freight?
You see costs change with distance, shipment size, transportation mode, and timing. Fuel prices and seasonal demand also impact rates. Packing your goods efficiently helps you save money.
See Also
Enhancing Global Operations With Creative Logistics Strategies
PGL Specializes in LTL and FTL Shipping Services
Simplifying U.S. Air Freight Exports With PGL Services
PGL Offers Nationwide Ocean Freight Export Solutions
Comprehensive Export Options Including Full Container and LCL by PGL
